17 April 2022
Transform Data in your Warehouse using dbt, Airflow, and Redshift
tags: Big Data - AWS - Airflow - dbt - Redshift
Data Build Tool (better and simply known as “dbt”) is a fantastic tool that will help you make your transformation processes much simpler. dbt fits nicely into the modern Business Intelligence stack, coupling with products like Redshift, Snowflake, Databricks, and BigQuery. Its main function is to take your custom code, compile it into SQL, and then run it against your warehouse. The code is a combination of SQL and Jinja (a templating language used in Python).
You might already use Apache Airflow in your stack to orchestrate your data pipelines. But if this is not the case, I strongly recommend using Airflow. AWS provides a managed version of Airflow that you can create in few minutes and it will be fully integrated with other AWS services like Lambda or Redshift.
In this blog post, I will explain how you can run all of your transformation processes using dbt directly on Airflow and take advantage of all its features. All of the code in this blog post is available at this GitHub repository.
AWS Services and Architecture
The beauty of AWS is that it provides us all of the services that we need in order to build the Airflow platform. That saves us time and headaches of hosting and configuration, and instead allows us to focus on the fun parts of this project.
The architecture leverages mature AWS services and the flow is pretty simple. Here is a diagram to summarize:
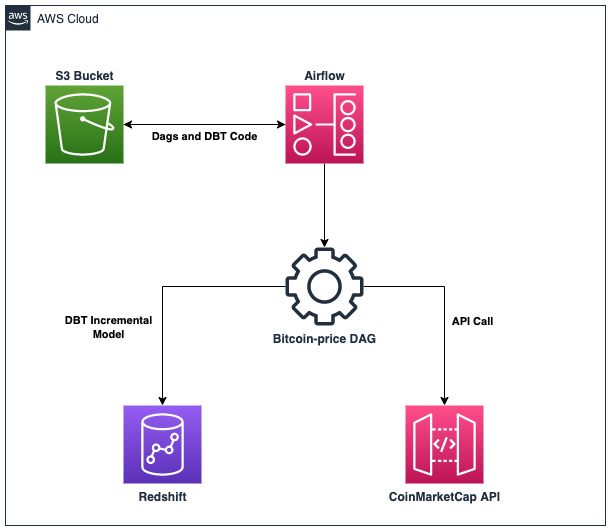
Airflow DAG
The DAG will be divided into two (2) tasks and will run every five (5) minutes:
- Get a Bitcoin quote from the CoinMarketCap API and save it to Redshift
- Run the incremental dbt model
from airflow.models import DAG, Variable
from airflow.operators.python import PythonOperator
from airflow_dbt.operators.dbt_operator import DbtRunOperator
from requests import Session
from datetime import datetime
import json
import awswrangler as wr
import pandas as pd
def save_quote():
# Set headers
url = "https://pro-api.coinmarketcap.com/v1/cryptocurrency/quotes/latest?symbol=BTC"
headers = {
"Accepts": "application/json",
"X-CMC_PRO_API_KEY": Variable.get('API_KEY')
}
# Get quote
session = Session()
session.headers.update(headers)
data = json.loads(session.get(url).text)
# Load quote to df
df = pd.DataFrame(data["data"]["BTC"]["quote"]["USD"], index=['i',])
# Add audit columns
df['inserted_at'] = datetime.now()
# Save quote to Redshift
con = wr.redshift.connect_temp(cluster_identifier="blog-dbt-airflow", user="awsuser", database="dev", auto_create=False)
wr.redshift.to_sql(
df=df,
table="quote",
schema="public",
con=con
)
con.close()
with DAG("bitcoin-price", schedule_interval="*/5 * * * *", start_date=datetime(2022, 4, 5), catchup=False) as dag:
save_quote_task = PythonOperator(task_id="save-quote",
python_callable=save_quote)
dbt_task = DbtRunOperator(task_id="dbt",
dbt_bin="/usr/local/airflow/.local/bin/dbt",
profiles_dir="/usr/local/airflow/dags/blog_dbt_airflow/",
dir="/usr/local/airflow/dags/blog_dbt_airflow/",
models="quote")
save_quote_task >> dbt_task
Running dbt directly on Airflow is possible using the operators from this GitHub project. In this case, we will simply use the DbtRunOperator and specify where dbt is installed. The CoinMarketCap API Key is stored as an Airflow variable to avoid having it hardcoded.
dbt Model
The dbt model is pretty simple since the goal of this project is to show how dbt can run directly on Airflow instead of an ECS task, for example. All of the dbt code will be stored directly in the S3 Bucket so the Airflow DAG can easily access it.
Here is the incremental dbt model that will simply add new rows based on the column inserted_at:
SELECT * FROM public.quote
The target schema for this model is dbt. For more details, you can take a look at the file profiles.yml. Few properties from the file dbt_project.yml were also changed because of read-only file system (packages-install-path, log-path and target-path).
Deployment using AWS CDK
The whole stack can be deployed with CDK using the command cdk deploy. It will generate a CloudFormation template and execute it.
Stack’s components:
- Clean VPC
- S3 bucket prefilled with Airflow DAG and dbt code
- IAM role with mandatory permissions
- Redshift cluster
- Airflow
Feel free to clone my GitHub repository that has the stack already configured.
Once the whole stack is deployed and the Airflow instance is running, the DAG can be turned on and will start collecting data and transforming it.
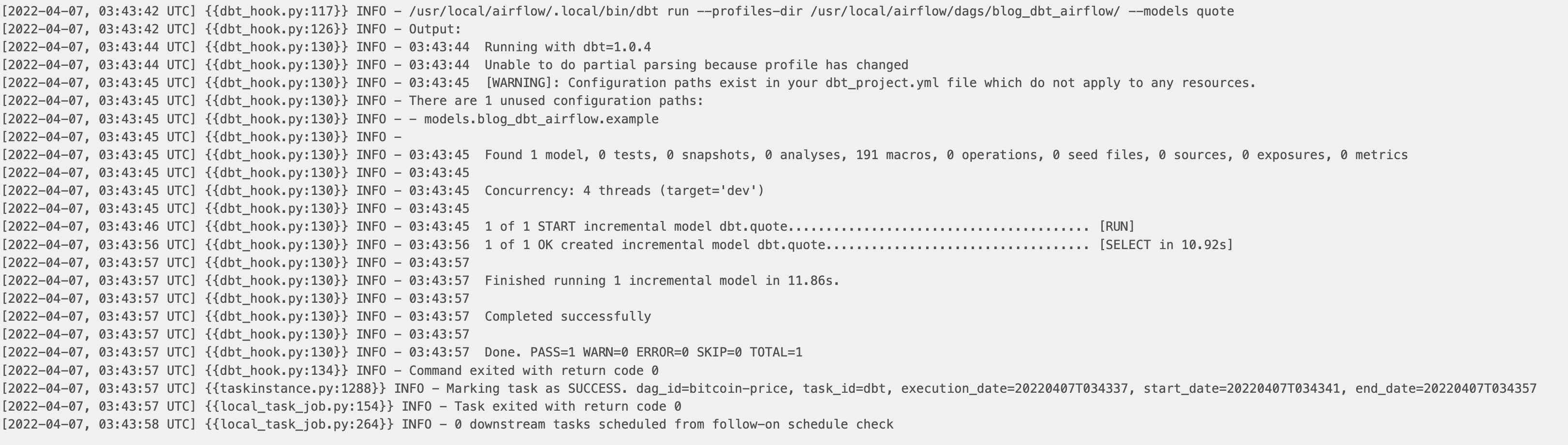
You can see the dbt logs directly on the Airflow UI:
Conclusion
Creating a project that uses dbt and Airflow was relatively easy using the available AWS services. CDK allows you to focus on the architecture design instead of wasting time on trivial things like configurations, permissions, and networking.
With the dbt Operator, it is rather easy to run your dbt models in your Airflow data pipelines without having to start an ECS task, for example. And your dbt project can be directly updated on Airflow using the S3 bucket.
Need help using the latest authentication technology? Or perhaps you are looking to modernize your legacy systems using these newer tools? Ippon can help! Send us a line at contact@ippon.tech.